The Firewall table displays all the firewall rules configured for different interfaces.
Note: If you import a configuration for a chain through CLI, the rules defined for the specified chain(s) will be overridden by the imported configuration. For example, if you are importing configuration For the INPUT and OUTPUT chains, the FORWARD chain will not be changed, only the INPUT and OUTPUT chains are updated.
Add a Chain
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- Click Add (displays dialog).
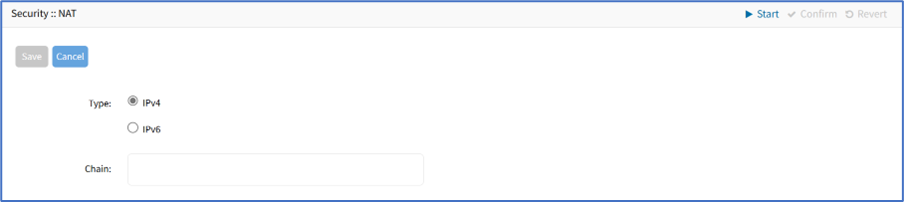
- On Type menu, select one:
- IPv4 radio button
- IPv6 radio button
- Enter Chain (name of this chain).
- Click Save.
Delete a Chain
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- Select the checkbox next to the name to be deleted.
- Click Delete.
- On the confirmation dialog, click OK.
Change Chain Policy
NOTE
The policy cannot be changed for user custom chains. The policy can only be changed for default chains.
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, select the checkbox of Chain.
- Click Change Policy (displays dialog). On Policy drop-down, select one (ACCEPT, DROP).
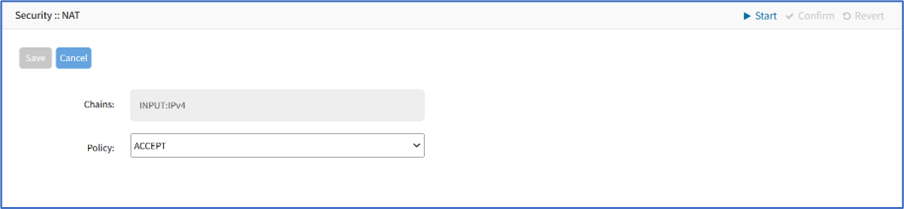
- Click Save.
Manage a Chain
To manage chain functions/settings, click on the name in the Chain column (displays dialog).
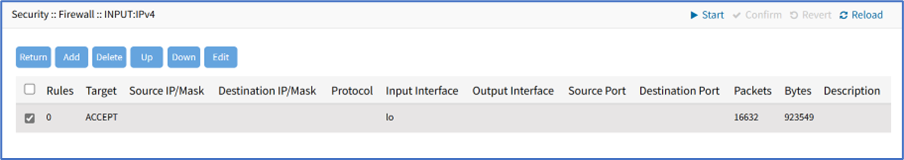
Add Rule
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, locate and click on the name (displays dialog).
- Click Add (displays dialog).
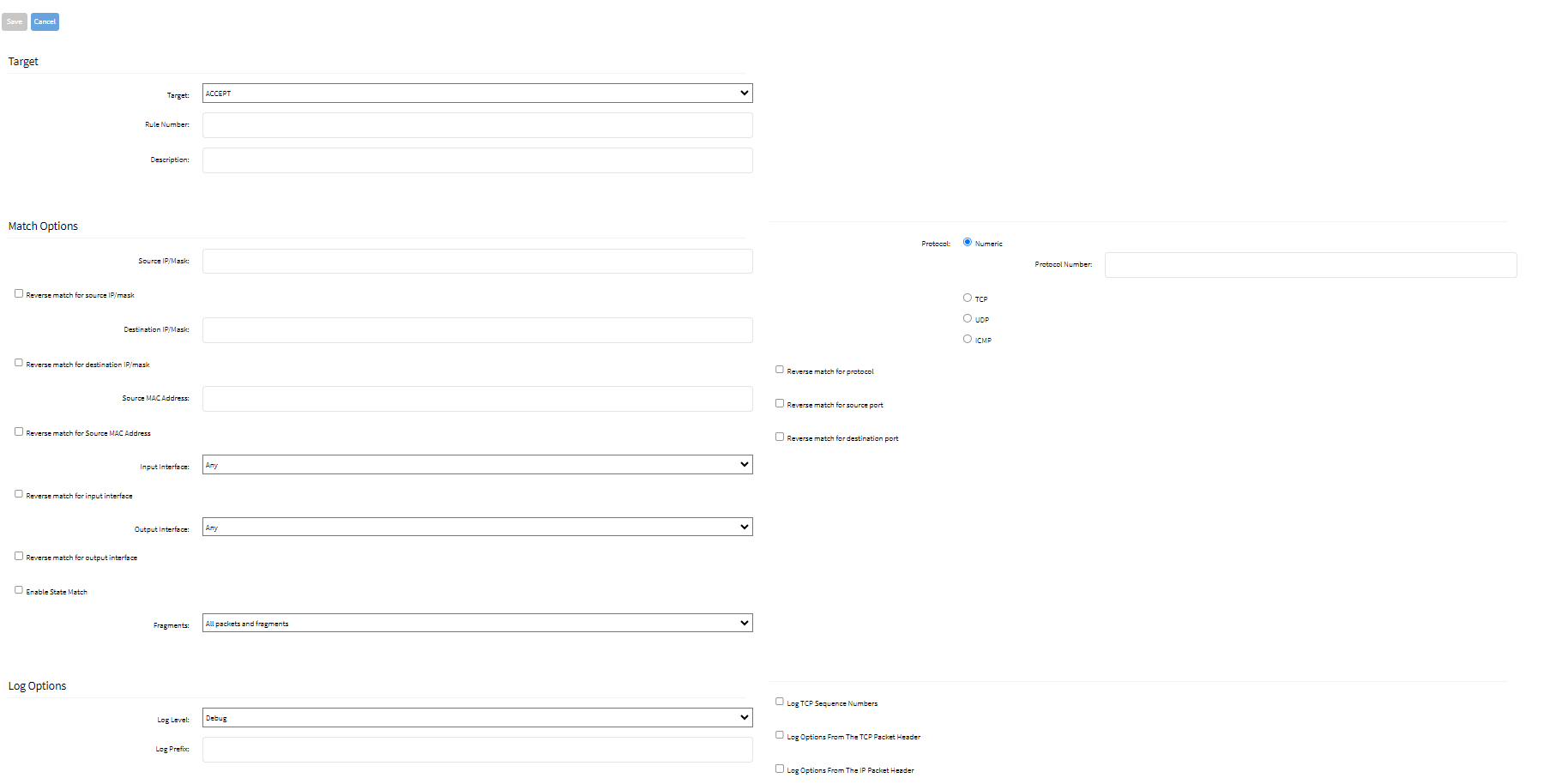
- On the Target menu, on the Target drop-down, select one (ACCEPT, DROP, REJECT, LOG, RETURN). Enter the Rule Number and Description.
- If REJECT is selected, the Reject Options menu displays:
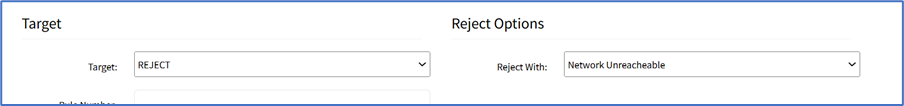
- On Reject With drop-down, select one (Network Unreachable, Host Unreachable, Port Unreachable, Protocol Unreachable, Network Prohibited, Host Prohibited, Administratively Prohibited, TCP Reset).
- If REJECT is selected, the Reject Options menu displays:
- On the Match Options menu:
- Enter Source IP/Mask
- Select Reverse match for source IP/mask checkbox
- Enter Destination IP/Mask
- Select Reverse match for destination IP/mask checkbox
- Enter Source MAC Address
- Select Reverse match for source MAC address checkboxNote: The Source MAC Address and Reverse Match for the source MAC Address fields are applicable only for Input, PREROUTING, and FORWARD chains.
- From the Input Interface drop-down list, select one. The list contains all the available interfaces such as eth0, eth1, loopback1, custom, etc.
 Note: The Source MAC Address and Reverse Match for the source MAC Address fields are applicable only for Input, PREROUTING, and FORWARD chains.
Note: The Source MAC Address and Reverse Match for the source MAC Address fields are applicable only for Input, PREROUTING, and FORWARD chains.- If you want to add an interface that is not listed, select Custom. You can create any custom interface.
- In the Custom Input Interface field, specify the name of the interface.
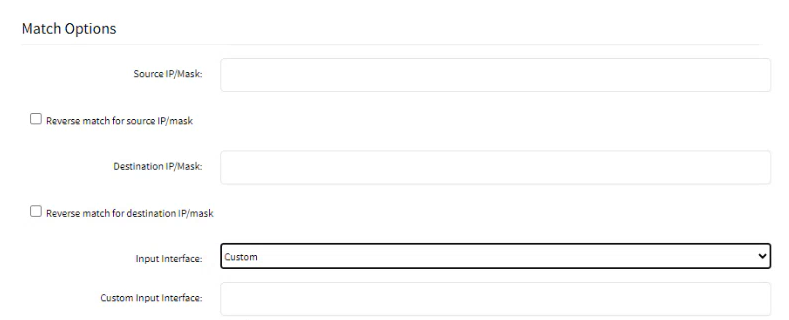
The user can later go to Network::Connections and click Add, to add the Custom Input Interface mentioned under the Custom Input Interface
- Select Reverse match for the input interface checkbox
- On the Output Interface drop-down, select the required interface. If an interface is not listed or does not exist, you can use the Custom option from the drop-down list to specify the name of the interface:
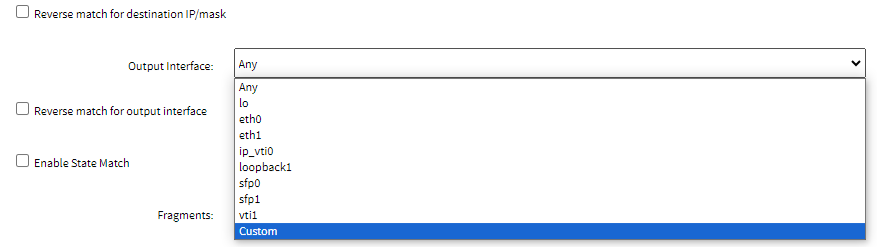 Note: The Source MAC Address and Reverse Match for the source MAC Address fields are applicable only for Output, POSTROUTING, and FORWARD chains.
Note: The Source MAC Address and Reverse Match for the source MAC Address fields are applicable only for Output, POSTROUTING, and FORWARD chains. - In the Custom Output Interface field, specify the name of the interface.

The user can later go to Network::Connections and click Add, to add the Interface mentioned under the Custom Output Interface. - Select Reverse match for the output interface checkbox
- Select Enable State Match checkbox (displays options – one or more can be selected):
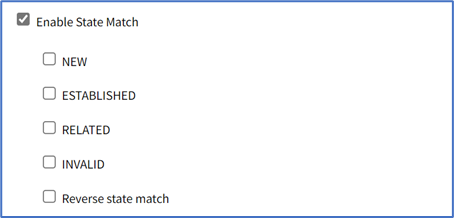
- NEW checkbox
- ESTABLISHED checkbox
- RELATED checkbox
- INVALID checkbox
- Reverse state match checkbox
- On Fragments drop-down, select one (All packets and fragments, Unfragmented packets and 1st packets, 2nd and further packets)
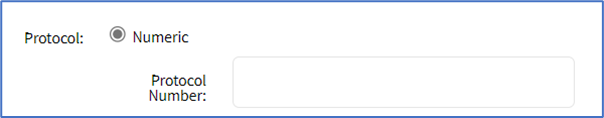
- On the Protocol menu, select one:
- Numeric radio button (expands dialog). Enter the Protocol Number.
- TCP radio button (expands dialog).
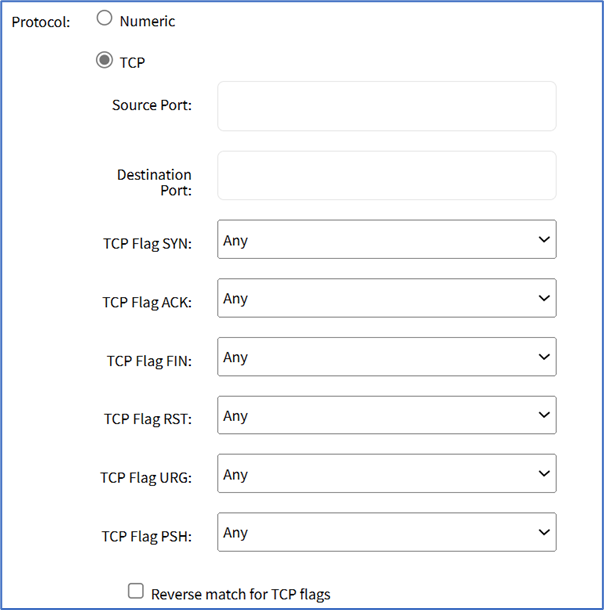
- Enter Source Port.
- Enter Destination Port.
- TCP Flag SYN drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- TCP Flag ACK drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- TCP Flag FIN drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- TCP Flag RST drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- TCP Flag URG drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- TCP Flag PSH drop-down, select one (Any, Set, Unset)
- Reverse Match for TCP Flags checkbox
- UDP radio button (expands dialog)
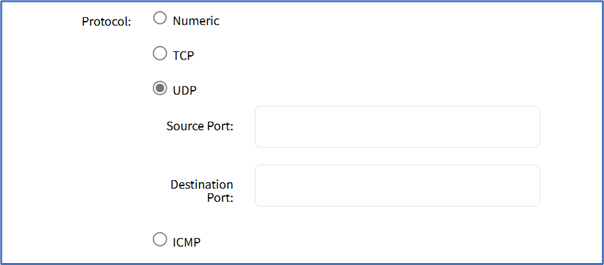
- Enter Source Port
- Enter Destination Port
- ICMP radio button (expands dialog)
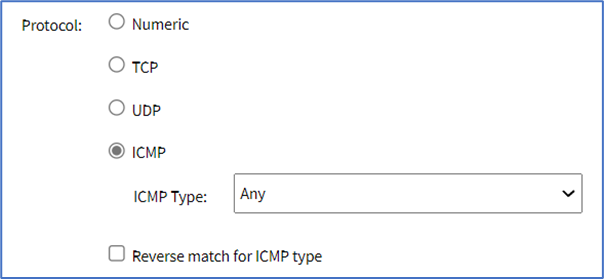
- On ICMP Type drop-down, select one (Any, Echo-Reply, Destination Unreachable, Network Unreachable, Host Unreachable, Protocol Unreachable, Port Unreachable, Fragmentation Needed, Source Route Failed, Network Unknown, Host Unknown, Network Prohibited, Host Prohibited, TOS Network Unreachable, TOS Host Unreachable, Communication Prohibited, Host Precedence Violation, Precedence Cutoff, Source Quench, Redirect, Network Redirect, Host Redirect, TOS Network Redirect, TOS Host Redirect, Echo Request, Router Advertisement, Router Solicitation, Time Exceeded, TTL Zero During Transit, TTL Zero During Reassembly, Parameter Problem, Bad IP Header, Required Option Missing, Timestamp Request, Timestamp Reply, Address Mask Request, Address Mask Reply)
- Select Reverse match for ICMP type checkbox
- Select Reverse match for the protocol checkbox
- Select Reverse match for source port checkbox
- Select Reverse match for destination port checkbox
- Numeric radio button (expands dialog). Enter the Protocol Number.
- From the Log Options menu:
- From the Log Level drop-down list, select one (Debug, Info, Notice, Warning, Error, Critical, Alert, Emergency)
- Enter Log Prefix
- Select the Log TCP Sequence Numbers checkbox
- Select the Log Options from the TCP Packet Header checkbox
- Select the Log Options from the IP Packet Header checkbox
- Click Save.
Edit Chain
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, locate and click on the checkbox.
- Click Edit (displays dialog).
- Make changes, as needed.
- Click Save.
Delete Chain
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, locate and select the checkbox on the name.
- Click Delete.
- On the confirmation dialog, click OK.
Move Chain Up
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, locate and select the checkbox on the name.
- Click Up to move up.
Move Chain Down
- Go to Security :: Firewall.
- In the Chain column, locate and select the checkbox on the name.
- Click Down to move down.