This chapter covers the security aspects from a hardware perspective.
TPM (Trusted Platform Module)
Trusted Platform Module (TPM, also known as ISO/IEC 11889) is an international standard for a secure crypto processor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. It is a hardware used for operations of encryption and its architecture is defined by the Trusted Computing Group (TCG), an international group for standardization of Trusted Computing.
TPM Use cases on the Nodegrid: TPM can be used as a crypto processor, key generator, secure storage, and unique hardware identifier in applications like:
Password-protected storage: TPM NVRAM can be used by the application to store a secret protected by a password.
Boot Integrity protected storage: TPM NVRAM can be used by the application to store a secret protected by a specific PCR value.
Drive cryptography: Keys generated in TPM can be used to secure data encrypting keys in software cryptography solutions. In Self Encrypting Drive applications, using OPAL, TPM NVRAM can be used to store the password to unlock the OPAL Drive.
Authentication: TPM private keys may be used to authenticate the platform in any enrollment process.
TPM Random number generator can be used as a trusted password generator.
UEFI Boot with signed OS – Password Protected Boot and BIOS
To guarantee the maximum level of security provided by the secure boot mechanism, we follow the Secure Boot verification Flow (Secure Chain):
BIOS Configuration is password protected. (*)
UEFI Secure Boot checks if the Bootloader binary is signed with a valid certificate installed in the BIOS Authorized Keys Database.
Signed password-protected GRUB is loaded. (*)
GRUB checks config file, kernel, initrd, and other static OS files are signed using GRUB GPG Key;
OS is loaded.
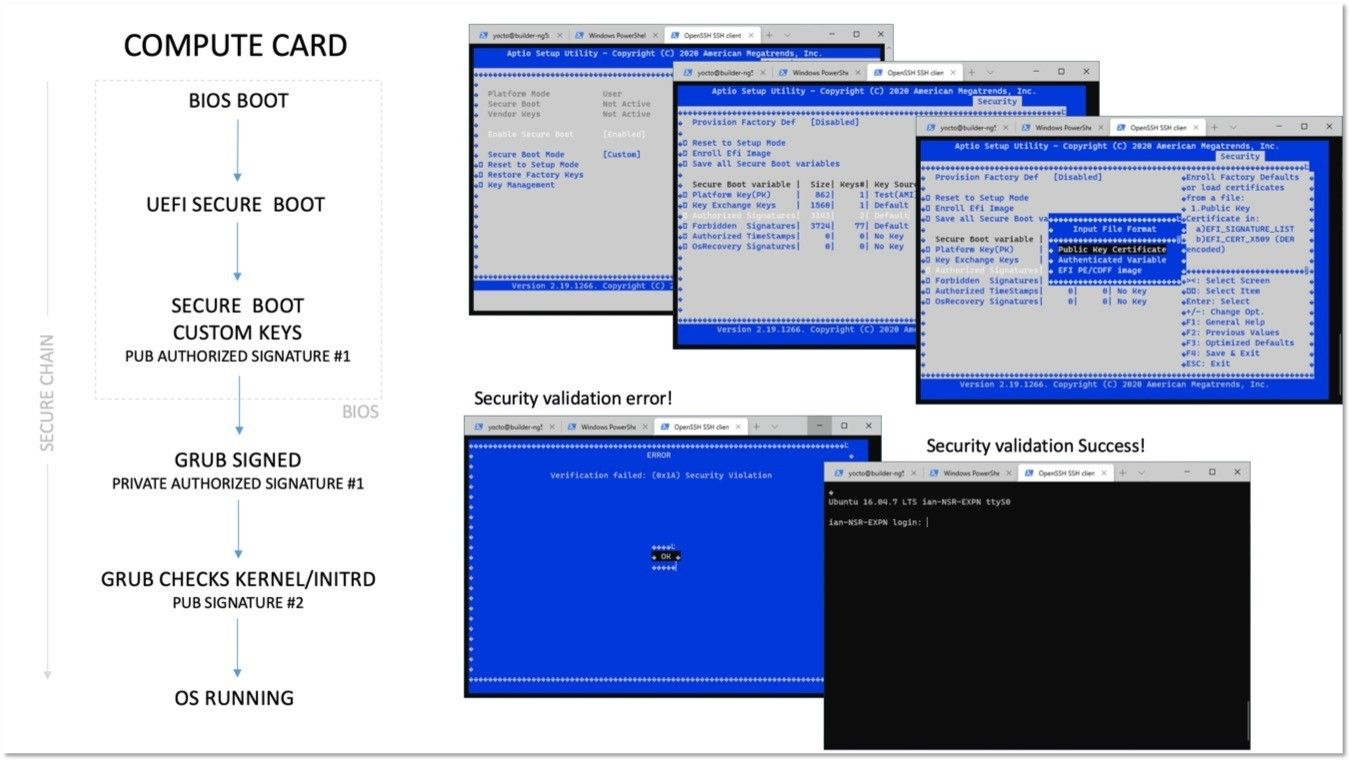
(*): This feature allows Nodegrid OS (via CLI or WebUI) to communicate with the BIOS to enable the BIOS password to prevent unauthorized changes on it. The same password will also protect Grub from unauthorized changes. During a reboot of the unit, without any interaction with the user, the Nodegrid appliance will boot normally. If the administrator user needs to make any changes in the BIOS or Grub, a password will be required. This password-protected boot will prevent any unauthorized user to try and edit the system.
Secure Erase
There are 2 effective and secure ways to erase the Nodegrid appliance’s system configuration:
By following the Letter of Volatility (refer to Appendix D (see section Appendices))
It is non-intrusive.
It is executed via a built-in hardware feature of the SSD that allows to erasing of all sectors on the entire SSD flash unit.
Nodegrid Serial Console implements ATA secure erase via the hdparm tool.
See Appendix B (see section Appendices) for the Letter of Volatility
“Sanitizing a storage device using ATA Secure Erase
Sanitizing is the removal of sensitive data from a system or storage device with the intent That the data cannot be reconstructed by any known technique. For data residing on hard drives and solid-state drives (SSD), a method known as ATA Secure Erase is the MOST effective.
ATA Secure Erase is part of the ANSI ATA specification and When Implemented Correctly, wipes the entire contents of a drive at the hardware level Instead of through software tools. Software tools over-write data on hard drives and SSDs, often through multiple passes; over-writing The Problem with SSDs Is That Such software tools cannot access all the storage areas on an SSD, leaving behind blocks of data in the service regions of the drive (examples: Bad Blocks, Wear-Leveling Blocks, etc.)
When an ATA Secure Erase (SE) command is issued against an SSD's built-in controller That properly supports it, the SSD controller resets all its storage cells as empty (releasing stored electrons) - just THUS restoring the SSD to factory default settings and write performance. When implemented properly, SE will process all regions Including the protected storage service regions of the half.
Secure Erase is Recognized by the US National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST), as an effective and secure way to meet legal requirements for data sanitization attacks up to laboratory level.”
Source: http://www.kingston.com/us/community/articledetail?ArticleId=10
By removing the mSATA card from the NSC motherboard, and shredding it;
See the instructions below:
Turn the NSC off.
Open the unit by removing the screws and the lid.
Identify the mSATA card (see picture) – located by the fans, on the corner of the unit.
Remove the 2 screws, and then remove the card from the slot.

Self-Encrypting Drive (SED)
Hardware-based full-disk encryption (HB-FDE) is now available from many hard disk vendors, becoming increasingly common. Self-Encrypting Drive (SED) refers to SSDs or SSDs with built-in full-disk encryption.
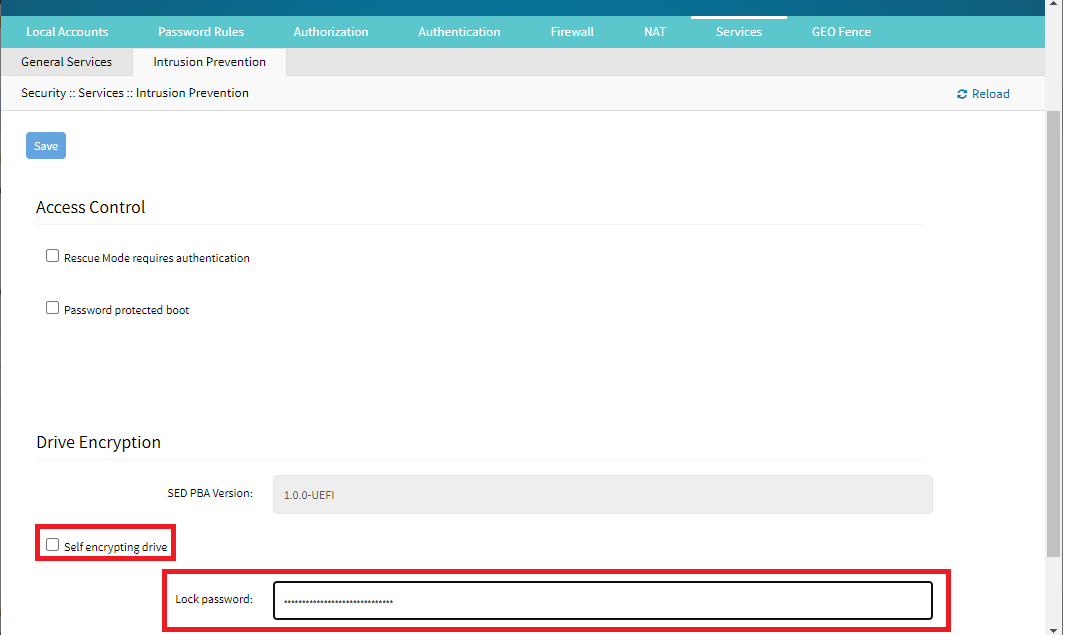
The SED feature provides data privacy security against SSD theft. The customer can enable SSD data encryption based on an authentication password. A PBA (Pre-Boot Authentication) is responsible for unlocking the drive on boot.
SED is easy to set up (compared to software-based encryption), notably transparent to the user, presents increased performance (CPU is freed up from encryption/decryption calculations), an optimally fast and secure disk erasure (sanitation), and protection against alternative boot methods due to the possibility to encrypt the MBR (Master Boot Record), rendering the drive inaccessible before pre-boot authentication.
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM, also known as ISO/IEC 11889) is an international standard for a secure crypto processor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. Pre-Boot Authentication (PBA) or Power-On Authentication (POA) serves as an extension of the BIOS, UEFI or boot firmware and guarantees a secure, tamper-proof environment external to the operating system as a trusted authentication layer.
The PBA prevents anything being read from the hard disk such as the operating system until the user has confirmed they have the correct password or other credentials. The SED password is stored in the TPM non-volatile memory.
The SED feature is currently supported on the models:
NSCP
NSC-S
Net SR
Gate SR
Bold SR
Link SR
Mini SR
NOTES:
When enabled, PXE (Preboot eXecution Environment) will be disabled for security reasons. Boot order will be set to SSD only, for security reasons.
Enabling “password protected boot” (BIOS password) is recommended for maximum security.
SED is available exclusively in UEFI Mode.
Be sure to store the Lock password. It will be required for disabling SED when required.
Intel QuickAssist Technology (Intel QAT)
The NSR TOP and GSR UPG models include the Intel QuickAssist Technology (Intel QAT), which is a cryptographic accelerator device that can be used to accelerate and compress cryptographic workloads.
The integration of the IPsec with the Intel QAT allows offloading the IPsec encryption and decryption and improves network performance over IPSec VPN. For example, the Intel QAT provides symmetric cryptographic acceleration services that can be used to offload both the encryption/decryption and authentication processing tasks. Supported encryption algorithm includes AES-CBC and AES-CTR.