VRF (Virtual Routing Forward) is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within same Linux Operating System.
A VRF connection can be created to restrict network traffic going through selected interfaces to a specific routing table.
This feature currently supports limited use cases. For example, the Linux commands ip vrf exec … can be used by processes after configuring a VRF connection.
However, the VRF configuration does not guarantee that all processes in the system will use the routing tables. For example:
Managed devices will try to establish connections looking at default VRF routes only
VPN tunnels will be running on default VRF by default
IPSec can be configured to use a different VRF to establish tunnels
Network failover is not prepared to handle a VRF slave connection
Static routes page only adds routes in default VRF
ZPE Cloud, TACACS+, LDAP, RADIUS and Kerberos can only look up routes in default VRF
- Go to Network :: Connections.
- Click Add (displays dialog).
- Enter Name.
- On Type drop-down, select VRF (dialog changes).
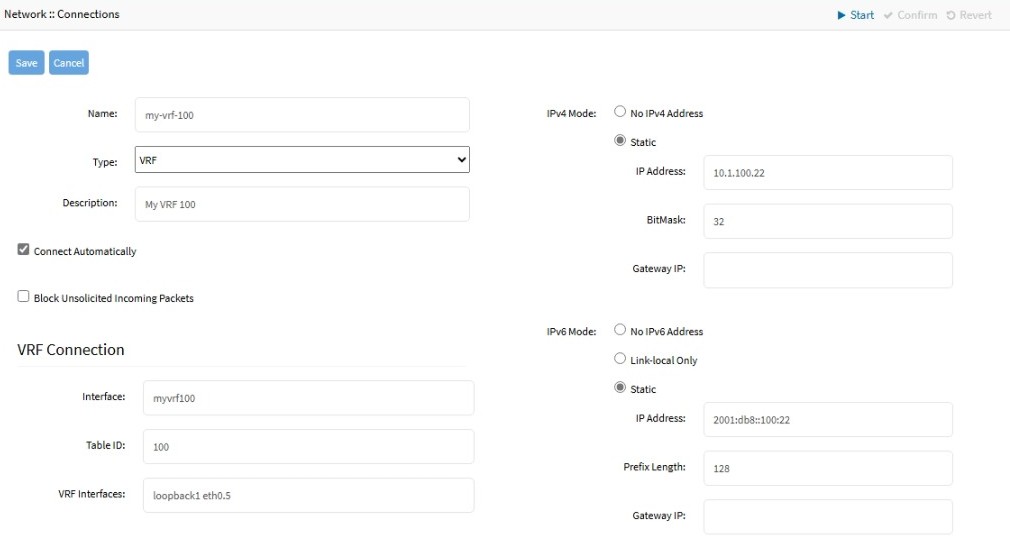
- Enter Description.
- If the Connect Automatically checkbox is selected, the connection is automatically established at startup.
- If Block Unsolicited Incoming Packets checkbox is selected, firewall rules will be created to automatically block all inbound connections on the interface.
- In the VRF Connectionmenu:
- Enter Interface to select the name of the new interface that will be created for this VRF. If empty, interface will be called vrfN, where N is a number starting at 0 and automatically incremented as needed.
- Table ID defines the identificator of the routing table associated to this VRF interface
- VRF Interfaces is a space-separated list of other OS interfaces that will be slaves to the created VRF interface, having traffic respecting the specified routing table
- In IPv4 Mode menu, enter details:
- No IPv4 Address radio button
- Static radio button (if selected, expands dialog). Enter IP Address, BitMask. and (optional) Gateway IP.
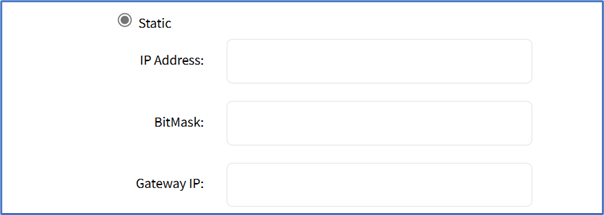
- (optional) IPv4 DNS Server
- IPv4 DNS Search (defines a domain name for DNS lookups)
- IPv4 Default Route Metric
- Ignore obtained IPv4 Default Gateway checkbox
- Ignore obtained DNS server checkbox
- In IPv6 Mode menu, enter details:
- No IPv6 Address radio button
- Link local Only radio button.
- If Static radio button is selected (displays menu). Enter IP Address, Prefix Length, and (optional) Gateway IP.
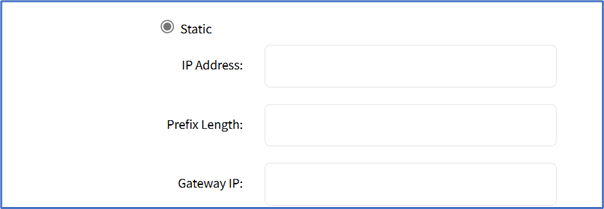
- No IPv6 Address radio button
- Click Save.